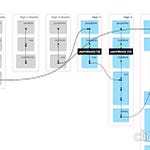
Partitioning and bucketing are essential techniques in Apache Spark that help optimize data processing and storage.
Partitioning
Partitioning refers to dividing a large dataset into smaller, more manageable parts (partitions) across a cluster's nodes. Each partition can be processed independently, allowing parallelism and efficient data distribution.
Why to use it?
Improves parallelism: Ensures better utilization of cluster resources.
Reduces data shuffling: By colocating data that is frequently accessed together.
Optimizes joins and aggregations: Data with the same partition key stays in the same node.
Where Not to Use
Small datasets: Partitioning increases overhead when the data is small.
Dynamic keys: Partitioning may not be efficient when keys are dynamic and unpredictable.
Examples
RDD Example
from pyspark import SparkContext
sc = SparkContext("local", "Partitioning Example")
Create an RDD
data = [("USA", 1), ("India", 2), ("USA", 3), ("UK", 4), ("India", 5)]rdd = sc.parallelize(data)
Partition by key
partitioned_rdd = rdd.partitionBy(3) # 3 partitions
Inspect partitions
print(partitioned_rdd.glom().collect())DataFrame Example
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Partitioning Example").getOrCreate()
***Create a DataFrame***
data = [("USA", 1), ("India", 2), ("USA", 3), ("UK", 4), ("India", 5)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Country", "Value"])
***Write with partitioning***
df.write.partitionBy("Country").parquet("/tmp/partitioned_data")Bucketing
Bucketing distributes data into a fixed number of buckets based on a hash of the bucketing column(s). Unlike partitioning, it doesn’t physically separate the data but ensures logical organization within partitions.
Why to use it?
Optimizes joins: Pre-bucketing datasets on the join key avoids shuffling.
Reduces shuffle: When aggregating data using the bucket column.
Fixed-size group: Ideal when the data is evenly distributed.
Where Not to Use
Skewed data: Bucketing may lead to uneven distribution, causing performance bottlenecks.
Frequent changes: Bucketing requires rewriting data for schema or bucket count changes.
Examples
RDD Example
from pyspark import SparkContext, StorageLevel
sc = SparkContext("local", "Bucketing Example")
***Create an RDD***
data = [("USA", 1), ("India", 2), ("USA", 3), ("UK", 4), ("India", 5)]
rdd = sc.parallelize(data)
***Custom bucketing function***
def custom_bucketing(key):return hash(key) % 2 # 2 buckets
***Apply bucketing***
bucketed_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: (custom_bucketing(x[0]), x)).persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK)
print(bucketed_rdd.collect())DataFrame Example
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Bucketing Example").getOrCreate()
***Create a DataFrame***
data = [("USA", 1), ("India", 2), ("USA", 3), ("UK", 4), ("India", 5)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Country", "Value"])
***Write with bucketing***
df.write.bucketBy(2, "Country").sortBy("Value").saveAsTable("bucketed_table")Custom Partitioning and Bucketing
Custom Partitioning
Custom partitioning involves creating a user-defined partitioning logic.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Custom Partitioning").getOrCreate()
***Define a custom partitioner***
class CustomPartitioner:
def init(self, num_partitions):self.num_partitions = num_partitions
def getPartition(self, key):
return hash(key) % self.num_partitions
***Apply custom partitioner***
data = [("USA", 1), ("India", 2), ("USA", 3), ("UK", 4), ("India", 5)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Country", "Value"])
df.rdd.partitionBy(3, lambda key: CustomPartitioner(3).getPartition(key))Custom Bucketing
Custom bucketing involves implementing a specific logic to hash and distribute data into buckets.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Custom Bucketing").getOrCreate()
data = [("USA", 1), ("India", 2), ("USA", 3), ("UK", 4), ("India", 5)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Country", "Value"])
***Write custom bucketed table***
df.write.bucketBy(3, "Country").sortBy("Value").saveAsTable("custom_bucketed_table")Combining Partitioning and Bucketing
You can combine partitioning and bucketing for optimized storage and processing.
***Combining partitioning and bucketing***
df.write.partitionBy("Country").bucketBy(2, "Value").saveAsTable("partitioned_bucketed_table")Summary
Partitioning is great for splitting data across nodes, reducing shuffling for common access patterns.
Bucketing is ideal for fixed, logical grouping of data within partitions.
Use custom partitioning and bucketing when default options don’t suit your specific use cases.